Space Waves: Exploring the Invisible Forces Shaping the Universe
Introduction
Space waves are the invisible yet powerful forces that travel across the cosmos, carrying vital information about the universe’s most mysterious processes. From electromagnetic radiation to gravitational ripples, these waves help us explore and understand celestial phenomena that are otherwise beyond human perception. Scientists have long been fascinated by these waves, as they offer critical insights into the origins of the universe, the nature of black holes, and the dynamics of cosmic events.
The discovery and study of space waves represent one of the most profound achievements in modern astrophysics. Over the past century, advances in technology have allowed us to detect and analyze these waves with remarkable precision. From radio waves to gamma rays and from gravitational waves to plasma disturbances, each type of space wave tells a unique story about the cosmos. Understanding these waves is essential for unlocking the secrets of the universe and pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.
Types of Space Waves

Electromagnetic Waves in Space
Electromagnetic waves are the most familiar form of space waves and play a fundamental role in our understanding of the cosmos. These waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields and can travel through the vacuum of space at the speed of light. The electromagnetic spectrum is vast and diverse, encompassing a range of wavelengths and frequencies, from long radio waves to short gamma rays.
Each segment of the electromagnetic spectrum reveals different aspects of the universe. Radio waves, for instance, allow astronomers to map the structure of galaxies and detect distant quasars. Infrared radiation can penetrate dust clouds, unveiling star-forming regions that are otherwise obscured. Visible light is the portion of the spectrum that human eyes can detect, while X-rays and gamma rays expose high-energy processes such as supernova explosions and black hole accretion disks. The ability to study electromagnetic waves across these different bands provides a comprehensive view of the universe’s complexity.
Space-based observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory have revolutionized our understanding of electromagnetic waves. By observing the cosmos without the interference of Earth’s atmosphere, these instruments capture clear and detailed images of celestial objects. The information gleaned from electromagnetic waves has reshaped our understanding of the universe, revealing its vastness, complexity, and the ongoing cosmic dance of matter and energy.
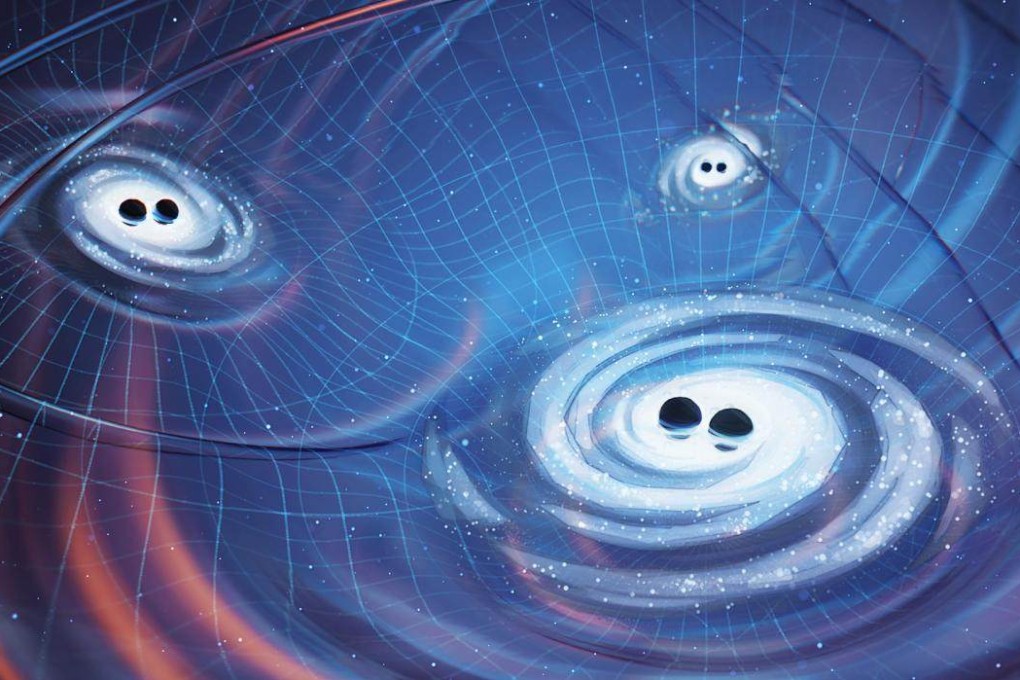
Gravitational Waves
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime caused by massive cosmic events, such as the collision of black holes or neutron stars. First predicted by Albert Einstein in 1916 as part of his General Theory of Relativity, these waves remained undetected for nearly a century. In 2015, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) made the groundbreaking detection of gravitational waves, confirming Einstein’s prediction and opening a new window into the cosmos.
Unlike electromagnetic waves, which require a medium to propagate, gravitational waves travel directly through the fabric of spacetime itself. When massive objects accelerate or merge, they generate these waves, which then spread out across the universe at the speed of light. By studying the properties of gravitational waves, scientists can investigate cataclysmic events that were previously invisible, such as black hole mergers and neutron star collisions.
The detection of gravitational waves has profound implications for astrophysics. It allows researchers to observe cosmic phenomena that do not emit light, providing a complementary perspective to traditional electromagnetic observations. Additionally, gravitational wave astronomy offers insights into the nature of spacetime, the behavior of extreme gravitational fields, and the possible existence of exotic objects like primordial black holes. Future advancements, including the launch of space-based interferometers like the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA), promise to expand our knowledge even further.
Plasma Waves
Plasma waves are another fascinating type of space wave that arises from the interaction of charged particles in space plasmas. Plasma, often called the fourth state of matter, consists of ions and free electrons and makes up the majority of the observable universe. In regions like the Sun’s corona, Earth’s magnetosphere, and interstellar space, plasma waves play a critical role in shaping cosmic environments.
These waves can take various forms, including electromagnetic plasma waves and electrostatic oscillations. Plasma waves are responsible for many phenomena, such as auroras, solar wind fluctuations, and space weather effects. When the solar wind—a stream of charged particles from the Sun—interacts with Earth’s magnetic field, it generates plasma waves that can disrupt satellite communications and pose risks to astronauts.
Scientists study plasma waves using space probes and ground-based observatories. Missions like NASA’s Parker Solar Probe and the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter aim to investigate plasma waves in the Sun’s atmosphere. Understanding plasma waves is vital for protecting space infrastructure and gaining deeper insights into cosmic plasma dynamics. These waves not only affect technological systems but also offer clues about the fundamental processes governing space environments.
Cosmic Rays and Particle Waves
Cosmic rays are highly energetic particles originating from outer space. Unlike other space waves, cosmic rays consist of subatomic particles—primarily protons and atomic nuclei—that travel at nearly the speed of light. These particles are produced by powerful astrophysical events such as supernova explosions, active galactic nuclei, and even the mysterious phenomena surrounding black holes.
When cosmic rays collide with Earth’s atmosphere, they create showers of secondary particles that scientists can detect using specialized observatories. Cosmic rays provide valuable information about the most energetic processes in the universe. For example, studying their composition and origin helps scientists trace back to the cosmic accelerators that produce them.
However, cosmic rays also pose challenges. They can damage electronic components in satellites, pose health risks to astronauts, and create background noise in particle detectors. Understanding cosmic rays requires collaboration across multiple scientific fields, including astrophysics, particle physics, and space science. Future missions aim to explore cosmic ray origins more deeply, offering new perspectives on the high-energy universe.
How Space Waves Are Detected and Measured
Space-Based Observatories
Space-based observatories are crucial for detecting and measuring space waves. Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope, the James Webb Space Telescope, and the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope provide unparalleled views of the universe. These observatories operate beyond Earth’s atmosphere, avoiding interference and capturing clearer, more detailed data.
Advanced detection methods include interferometry, which combines signals from multiple telescopes to enhance resolution. This technique is particularly important for studying distant objects and fine cosmic structures. Through space-based observatories, scientists continue to make groundbreaking discoveries, from exoplanets to the remnants of the Big Bang.
Conclusion
The study of space waves reveals the unseen forces shaping the universe and drives forward our understanding of cosmic phenomena. From electromagnetic radiation to gravitational ripples and plasma disturbances, these waves provide a window into the most profound mysteries of the cosmos. Advances in detection technology and interdisciplinary research are pushing the boundaries of our knowledge, promising new insights into the universe’s origins and future.
As our ability to observe and interpret space waves improves, so too does our capacity to unravel the complexities of the cosmos. Future missions and observatories will undoubtedly uncover even more about the dynamic and ever-changing nature of the universe. The exploration of space waves not only deepens our scientific understanding but also inspires curiosity and wonder about the vast and mysterious cosmos surrounding us.
FAQs
1. What are space waves?
Space waves refer to various types of waves that travel through space, including electromagnetic waves, gravitational waves, and plasma waves.
2. How are gravitational waves detected?
Gravitational waves are detected using interferometers like LIGO, which measure tiny distortions in spacetime caused by massive cosmic events.
3. Why is studying space waves important?
Understanding space waves helps us learn about the origins of the universe, detect black holes, and predict space weather that affects Earth.
4. What is the difference between electromagnetic and gravitational waves?
Electromagnetic waves are oscillations of electric and magnetic fields, while gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime caused by massive objects.
5. What future discoveries might space wave research lead to?
Future research could uncover new physical laws, detect exotic cosmic phenomena, and provide deeper insights into the nature of dark matter and energy.